$currentDate
$ currentDate运算符将字段的值设置为当前日期,可以是Date或时间戳。默认类型为日期。
$currentDate的形式为:
1
|
{ $currentDate: { <field1>: <typeSpecification1>, ... } }
|
可以是:
- 一个布尔值,true用于将字段值设置为当前日期作为Date,或者
- 明确指定类型的文档
{$type:“ timestamp”}或{$type:“ date”}。运算符区分大小写,并且仅接受小写的“时间戳”或小写的“日期”。
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
特性
如果该字段不存在,则$currentDate将该字段添加到文档中。
例子
customers使用以下文档创建样本集合:
1
2
3
|
db.customers.insertOne(
{ _id: 1, status: "a", lastModified: ISODate("2013-10-02T01:11:18.965Z") }
)
|
以下操作将lastModified字段更新为当前日期,将“cancellation.date”字段更新为当前时间戳,并将状态字段更新为“D”,将“cancellation.reason”更新为“用户请求”。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
db.customers.updateOne(
{ _id: 1 },
{
$currentDate: {
lastModified: true,
"cancellation.date": { $type: "timestamp" }
},
$set: {
"cancellation.reason": "user request",
status: "D"
}
}
)
|
更新后的文档类似于:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
{
"_id" : 1,
"status" : "D",
"lastModified" : ISODate("2020-01-22T21:21:41.052Z"),
"cancellation" : {
"date" : Timestamp(1579728101, 1),
"reason" : "user request"
}
}
|
Aggregation替代$currentDate
从4.2版开始,更新方法可以接受聚合管道。这样,可以使用聚合阶段$set和聚合变量 NOW(对于当前日期时间)和CLUSTER_TIME (对于当前时间戳记)将前面的示例重写为以下示例:
TIP:
- 要访问聚合变量,请在变量前加双美元符号$$并用引号引起来。
- CLUSTER_TIME 仅在副本集和分片群集上可用。
- 在整个管道中,NOW和CLUSTER_TIME值保持不变。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
db.customers.updateOne(
{ _id: 1 },
[
{ $set: { lastModified: "$$NOW", cancellation: {date: "$$CLUSTER_TIME", reason: "user request"}, status: "D" } }
]
)
|
查询应返回以下文档:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
{
"_id" : 1,
"status" : "D",
"lastModified" : ISODate("2020-01-22T21:02:18.994Z"),
"cancellation" : {
"date" : Timestamp(1579726934, 2),
"reason" : "user request"
}
}
|
$inc
$inc通过增加指定的值的字段,并具有以下形式:
1
|
{ $inc: { <field1>: <amount1>, <field2>: <amount2>, ... } }
|
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定,请使用点表示法。
特性
$inc运算符接受正值和负值。
如果该字段不存在,则$inc将创建该字段并将该字段设置为指定的值。
在具有空值的字段上使用$inc运算符将产生错误。
$inc是单个文档中的原子操作。
例子
考虑products包含以下文档的集合:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
{
_id: 1,
sku: "abc123",
quantity: 10,
metrics: {
orders: 2,
ratings: 3.5
}
}
|
以下update()操作使用$inc运算符将quantity字段减小2(即增加-2),并将"metrics.orders"字段增大1:
1
2
3
4
|
db.products.update(
{ sku: "abc123" },
{ $inc: { quantity: -2, "metrics.orders": 1 } }
)
|
更新后的文档类似于:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
{
"_id" : 1,
"sku" : "abc123",
"quantity" : 8,
"metrics" : {
"orders" : 3,
"ratings" : 3.5
}
}
|
$min
如果指定的值小于字段的当前值,则$min将字段的值更新为指定的值。 $min运算符可以使用BSON比较顺序来比较不同类型的值。
1
|
{ $min: { <field1>: <value1>, ... } }
|
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
特性
如果该字段不存在,则$min运算符会将字段设置为指定的值。
对于不同类型的值(例如数字和空值)之间的比较,$min使用BSON比较顺序。
例子
使用$min比较数字
考虑集合中的以下文档scores:
1
|
{ _id: 1, highScore: 800, lowScore: 200 }
|
文档的lowScore当前具有值200。以下操作使用$ min将200与指定值150进行比较,由于150小于200,因此将lowScore的值更新为150:
1
|
db.scores.update( { _id: 1 }, { $min: { lowScore: 150 } } )
|
scores现在,该集合包含以下修改后的文档:
1
|
{ _id: 1, highScore: 800, lowScore: 150 }
|
下一操作无效,因为该字段的当前值(lowScore即150)小于250:
1
|
db.scores.update( { _id: 1 }, { $min: { lowScore: 250 } } )
|
该文档在scores集合中保持不变:
1
|
{ _id: 1, highScore: 800, lowScore: 150 }
|
使用$min比较日期
考虑集合中的以下文档tags:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
{
_id: 1,
desc: "crafts",
dateEntered: ISODate("2013-10-01T05:00:00Z"),
dateExpired: ISODate("2013-10-01T16:38:16Z")
}
|
以下操作将dateEntered字段的当前值(即ISODate(“ 2013-10-01T05:00:00Z”))与指定的日期new Date(“ 2013-09-25”)进行比较,以确定是否更新该字段:
1
2
3
4
|
db.tags.update(
{ _id: 1 },
{ $min: { dateEntered: new Date("2013-09-25") } }
)
|
该操作将更新dateEntered字段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
{
_id: 1,
desc: "crafts",
dateEntered: ISODate("2013-09-25T00:00:00Z"),
dateExpired: ISODate("2013-10-01T16:38:16Z")
}
|
$max
如果指定的值大于字段的当前值,则$ max运算符会将字段的值更新为指定的值。 $ max运算符可以使用BSON比较顺序来比较不同类型的值。
$max运算符表达式的形式为:
1
|
{ $max: { <field1>: <value1>, ... } }
|
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
特性
如果该字段不存在,则$max操作员将该字段设置为指定值。
例子
使用$max比较数字
考虑集合中的以下文档scores:
1
|
{ _id: 1, highScore: 800, lowScore: 200 }
|
文档的highScore当前具有值800。以下操作使用$ max将800与指定值950进行比较,由于950大于800,因此将highScore的值更新为950。
1
|
db.scores.update( { _id: 1 }, { $max: { highScore: 950 } } )
|
scores现在,该集合包含以下修改后的文档:
1
|
{ _id: 1, highScore: 950, lowScore: 200 }
|
下一操作无效,因为该字段的当前值(highScore即950)大于870:
1
|
db.scores.update( { _id: 1 }, { $max: { highScore: 870 } } )
|
该文档在scores集合中保持不变:
1
|
{ _id: 1, highScore: 950, lowScore: 200 }
|
使用$max比较日期
考虑集合中的以下文档tags:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
{
_id: 1,
desc: "crafts",
dateEntered: ISODate("2013-10-01T05:00:00Z"),
dateExpired: ISODate("2013-10-01T16:38:16.163Z")
}
|
以下操作将dateExpired字段的当前值(即ISODate(“ 2013-10-01T16:38:16.163Z”))与指定的日期new Date(“ 2013-09-30”)进行比较,以确定是否更新field:
1
2
3
4
|
db.tags.update(
{ _id: 1 },
{ $max: { dateExpired: new Date("2013-09-30") } }
)
|
操作并没有更新的dateExpired领域:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
{
_id: 1,
desc: "decorative arts",
dateEntered: ISODate("2013-10-01T05:00:00Z"),
dateExpired: ISODate("2013-10-01T16:38:16.163Z")
}
|
$mul
将字段的值乘以数字。要指定 $mul表达式,请使用以下原型:
1
|
{ $mul: { <field1>: <number1>, ... } }
|
要更新的字段必须包含一个数字值。
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
特性
缺少字段
如果文档中不存在该字段,则$ mul将创建该字段并将其值设置为与乘法器相同的数字类型为零。
原子
$mul 是单个文档中的原子操作。
混合型
与混合数字类型(32位整数,64位整数,浮点数)的值相乘可能会导致数字类型转换。对于与混合数值类型的值相乘,将应用以下类型转换规则:
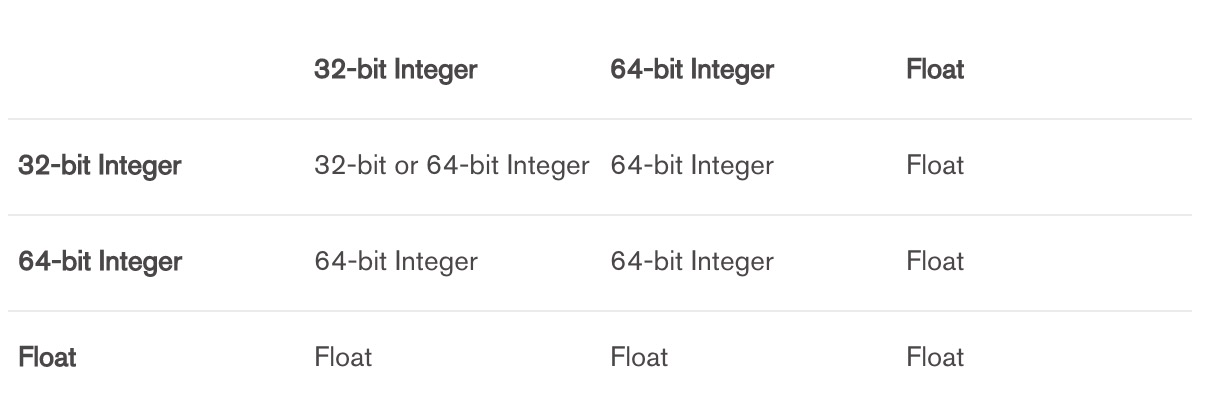
注意
- 如果两个32位整数的乘积超过了32位整数的最大值,则结果为64位整数。
- 超过64位整数最大值的任何类型的整数运算都会产生错误。
例子
乘以字段的值
考虑products包含以下文档的集合:
1
|
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "price" : NumberDecimal("10.99"), "qty" : 25 }
|
以下db.collection.update()操作使用$mul运算符将price by 1.25和qty字段乘以2:
1
2
3
4
|
db.products.update(
{ _id: 1 },
{ $mul: { price: NumberDecimal("1.25"), qty: 2 } }
)
|
该操作得出以下文档,其中价格的新值反映了原始值10.99乘以1.25,而数量的新值反映了原始值25乘以2:
1
|
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "price" : NumberDecimal("13.7375"), "qty" : 50 }
|
应用$mul操作员到一个不存在的字段
考虑products包含以下文档的集合:
1
|
{ _id: 2, item: "Unknown" }
|
以下db.collection.update()操作将$mul运算符应用于文档中不存在的字段价格来更新文档:
1
2
3
4
|
db.products.update(
{ _id: 2 },
{ $mul: { price: NumberLong(100) } }
)
|
该操作将导致以下文档的price字段设置为数值类型NumberLong的值0 ,该类型与乘数相同:
1
|
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "Unknown", "price" : NumberLong(0) }
|
乘法混合数值类型
考虑products包含以下文档的集合:
1
|
{ _id: 3, item: "XYZ", price: NumberLong(10) }
|
以下db.collection.update()操作使用$ mul运算符将价格字段NumberLong(10)中的值乘以NumberInt(5)
1
2
3
4
|
db.products.update(
{ _id: 3 },
{ $mul: { price: NumberInt(5) } }
)
|
该操作产生以下文档:
1
|
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "XYZ", "price" : NumberLong(50) }
|
该price字段中的值是NumberLong类型。
$rename
$rename运算符将更新字段名称,并具有以下格式
1
|
{$rename: { <field1>: <newName1>, <field2>: <newName2>, ... } }
|
新的字段名称必须与现有的字段名称不同。要在嵌入式文档中指定<field>,请使用点号。
考虑以下示例:
1
|
db.students.update( { _id: 1 }, { $rename: { 'nickname': 'alias', 'cell': 'mobile' } } )
|
此操作将字段重命名nickname为alias,并将字段重命名cell为mobile。
特性
$rename运算符在逻辑上执行旧名称和新名称的$unset,然后使用新名称执行$set操作。因此,该操作可能不会保留文档中字段的顺序;即重命名的字段可能会在文档中移动。
如果文档中已有一个带有<newName>的字段,则$rename运算符将删除该字段,并将指定的<field>重命名为<newName>。
如果文档中不存在要重命名的字段,则$rename不执行任何操作(即不执行任何操作)。
对于嵌入式文档中的字段,$rename运算符可以重命名这些字段,也可以将字段移入或移出嵌入式文档。如果这些字段在数组元素中,则$rename不起作用。
例子
集合students包含以下文档,其中某个字段的nmae拼写错误,即应为name:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
{
"_id": 1,
"alias": [ "The American Cincinnatus", "The American Fabius" ],
"mobile": "555-555-5555",
"nmae": { "first" : "george", "last" : "washington" }
}
{
"_id": 2,
"alias": [ "My dearest friend" ],
"mobile": "222-222-2222",
"nmae": { "first" : "abigail", "last" : "adams" }
}
{
"_id": 3,
"alias": [ "Amazing grace" ],
"mobile": "111-111-1111",
"nmae": { "first" : "grace", "last" : "hopper" }
}
|
本节中的示例将依次更新集合中的文档。
重命名字段
要重命名字段,请使用字段$rename的当前名称和新名称来调用运算符:
1
|
db.students.updateMany( {}, { $rename: { "nmae": "name" } } )
|
此操作将重命名字段nmae来name为集合中的所有文档:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
{
"_id": 1,
"alias": [ "The American Cincinnatus", "The American Fabius" ],
"mobile": "555-555-5555",
"name": { "first" : "george", "last" : "washington" }
}
{
"_id" : 2,
"alias" : [ "My dearest friend" ],
"mobile" : "222-222-2222",
"name" : { "first" : "abigail", "last" : "adams" }
}
{ "_id" : 3,
"alias" : [ "Amazing grace" ],
"mobile" : "111-111-1111",
"name" : { "first" : "grace", "last" : "hopper" } }
|
重命名嵌入文档中的字段
要重命名嵌入式文档中的字段,请使用点表示法调用$rename运算符以引用该字段。如果该字段将保留在同一嵌入式文档中,则还应使用新名称中的点号,如下所示:
1
|
db.students.update( { _id: 1 }, { $rename: { "name.first": "name.fname" } } )
|
此操作将嵌入式字段重命名first为fname:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
{
"_id" : 1,
"alias" : [ "The American Cincinnatus", "The American Fabius" ],
"mobile" : "555-555-5555",
"name" : { "fname" : "george", "last" : "washington" }
}
|
重命名一个不存在的字段
重命名字段并且现有字段名称引用的字段不存在时,$rename运算符不执行任何操作,如下所示:
1
|
db.students.update( { _id: 1 }, { $rename: { 'wife': 'spouse' } } )
|
此操作没有执行任何操作,因为没有名为wife的字段。
$set
该$set操作者更换一个字段与指定的值。
所述$set操作者的表达具有以下形式:
1
|
{ $set: { <field1>: <value1>, ... } }
|
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
特性
如果该字段不存在,$set则将添加具有指定值的新字段,前提是该新字段不违反类型约束。如果为不存在的字段指定点划线路径,$ set将根据需要创建嵌入的文档,以实现到该字段的点划线路径。
如果指定多个字段/值对,$set将更新或创建每个字段。
例子
考虑products包含以下文档的集合:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
{
_id: 100,
sku: "abc123",
quantity: 250,
instock: true,
reorder: false,
details: { model: "14Q2", make: "xyz" },
tags: [ "apparel", "clothing" ],
ratings: [ { by: "ijk", rating: 4 } ]
}
|
设置顶级字段
对于符合_id等于的条件的文档100,以下操作使用$set运算符更新quantity字段,details字段和tags 字段的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
db.products.update(
{ _id: 100 },
{ $set:
{
quantity: 500,
details: { model: "14Q3", make: "xyz" },
tags: [ "coats", "outerwear", "clothing" ]
}
}
)
|
该操作将值替换为:quantity为500。详细信息字段到新的嵌入式文档,而标签字段到新数组。
在嵌入式文档中设置字段
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
对于符合标准_id等于100的文档,以下操作将更新details文档中的make字段:
1
2
3
4
|
db.products.update(
{ _id: 100 },
{ $set: { "details.make": "zzz" } }
)
|
在数组中设置元素
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
对于符合等于_id等于100的条件的文档,以下操作将更新tags数组的第二个元素(数组索引为1)的值,以及ratings数组的第一个元素(array索引为0)中的rating字段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
db.products.update(
{ _id: 100 },
{ $set:
{
"tags.1": "rain gear",
"ratings.0.rating": 2
}
}
)
|
$setOnInsert
如果使用upsert:true进行更新操作会导致插入文档,则$setOnInsertm’k会将指定的值分配给文档中的字段。如果更新操作未导致插入,则$setOnInsert不执行任何操作。
您可以为db.collection.update()或db.collection.findAndModify()方法指定upsert选项。
1
2
3
4
5
|
db.collection.update(
<query>,
{ $setOnInsert: { <field1>: <value1>, ... } },
{ upsert: true }
)
|
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
例子
名为的集合products不包含任何文档。
然后,以下带有upsert:true的db.collection.update()插入新文档。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
db.products.update(
{ _id: 1 },
{
$set: { item: "apple" },
$setOnInsert: { defaultQty: 100 }
},
{ upsert: true }
)
|
MongoDB从<query>条件创建一个_id等于1的新文档,然后将$set和$setOnInsert操作应用于此文档。
该products集合包含新插入的文档:
1
|
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "apple", "defaultQty" : 100 }
|
如果具有upsert:true的db.collection.update()找到了匹配的文档,则MongoDB将执行更新,应用$set操作,但忽略$setOnInsert操作。
$unset
该$unset操作删除特定的领域。请考虑以下语法:
1
|
{ $unset: { <field1>: "", ... } }
|
$unset表达式中的指定值(即“”)不会影响该操作。
若要在嵌入式文档或数组中指定<field>,请使用点表示法。
特性
如果该字段不存在,则$unset不执行任何操作(即不执行任何操作)。
与$配合使用以匹配数组元素时,$unset会将匹配元素替换为null,而不是从数组中删除匹配元素。此特性使数组大小和元素位置保持一致。
例子
以下update()操作使用$unset运算符从字段sku值为未知的产品集合中的第一个文档中删除字段quantity和instock。
1
2
3
4
|
db.products.update(
{ sku: "unknown" },
{ $unset: { quantity: "", instock: "" } }
)
|
