应用场景
现在很多互联网公司还是在大量使用MySQL来存储各种类型的关系型数据。随着访问量和数据量的增长,开发者不得不考虑一些MySQL相关的新问题:
- 读写分离问题。由于前端应用访问量增加,单台MySQL不足以支撑整个系统的写入和查询操作。这时候,我们不得不将一些耗时的查询操作分散到多个slave上。
- 单表容量问题。如果在系统设计之初,没有考虑到分表问题。随着数据量的增长,单表容量越来越大。作者见过单表容量5亿条记录,然后一个简单的delete操作都会引起系统慢日志,而且有可能导致MySQL IO瞬发性的飙升。很多同学可能会想到,在查询的字段上加上索引,但当数据量增长到这么大的时候,即使加上索引效果也不明显了。归根结底,就是单表数据量太大,导致MySQL即使通过索引定位数据,仍然需要扫描很多记录。
- 数据库的运维问题。如果在代码中配置主库和从库host,系统运行当然也是没问题的。但这样大大增加了运维工作的压力,比如:MySQL数据库IO压力由于访问量的增加居高不下,DBA需要添加一台slave,这时候就不得不修改代码,然后打包并上线。还有很多非常实际的例子,在这就不一一列举。
- 连接池。前端应用频繁连接MySQL,由此给MySQL带来的额外性能消耗也是不容忽视的。如果通过增加一个连接池,每个DB缓存一定数量的MySQL连接,当有应用需要连接后端的MySQL,直接从连接池里取出一个已建好的连接来发送SQL请求,这样会大大加快数据查询速度。而且可以降低MySQL的性能消耗。
- SQL日志。在程序出现问题时,我们希望得到一些SQL日志,比如,什么时刻哪条SQL发送到哪一台DB上了。通过查看这种日志能够帮助我们快速定位问题。
面对这些问题,我们可以在客户端代码中逐一实现。但这样也会使得客户端越来越重,不那么灵活。kingshard对上述5类问题都有比较合适的解决方案。下面对kingshard的主要功能,逐个介绍并演示一下。
入门指南
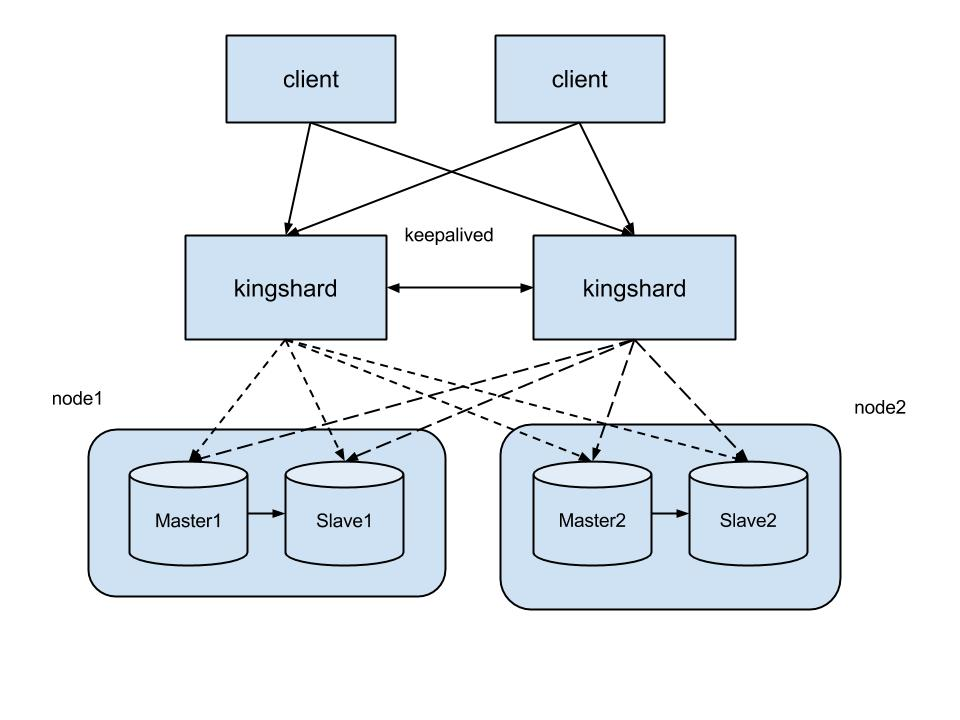
架构图
配置文件
下面给出一个配置文件范例,用户可以自行按照自己的需求逐项配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
|
# kingshard的地址和端口
addr : 0.0.0.0:9696
# 连接kingshard的用户名和密码的用户列表
-user_list:
-
user : kingshard
password : kingshard
#kingshard的web API 端口
web_addr : 0.0.0.0:9797
#调用API的用户名和密码
web_user : admin
web_password : admin
# log级别,[debug|info|warn|error],默认是error
log_level : debug
# 打开SQL日志,设置为on;关闭SQL日志,设置为off
log_sql : on
#如果设置了该项,则只输出SQL执行时间超过slow_log_time(ms)的SQL日志,不设置则输出全部SQL日志
slow_log_time : 100
#日志文件路径,如果不配置则会输出到终端。
log_path : /Users/flike/log
# sql黑名单文件路径
# 所有在该文件中的sql都会被kingshard拒绝转发
#blacklist_sql_file: /Users/flike/blacklist
# 只允许下面的IP列表连接kingshard,如果不配置则对连接kingshard的IP不做限制。
allow_ips: 127.0.0.1
# kingshard使用的字符集,如果不设置该选项,则kingshard使用utf8作为默认字符集
#proxy_charset: utf8mb4
# 一个node节点表示mysql集群的一个数据分片,包括一主多从(可以不配置从库)
nodes :
-
#node节点名字
name : node1
# 连接池中最大的空闲连接数,也就是kingshard最多与后端DB建立max_conns_limit个连接
max_conns_limit : 16
# kingshard连接该node中mysql的用户名和密码,master和slave的用户名和密码必须一致
user : kingshard
password : kingshard
# master的地址和端口
master : 127.0.0.1:3306
# slave的地址和端口,可不配置
#slave : 192.168.0.12@2,192.168.0.13@3
#kingshard在300秒内都连接不上mysql,kingshard则会下线该mysql
down_after_noalive : 300
-
name : node2
max_conns_limit : 16
user : kingshard
password : kingshard
master : 192.168.59.103:3307
slave :
down_after_noalive: 100
# 各用户的分表规则
schema_list :
-
#schema的所属用户名
user: kingshard
#分表分布的node名字
nodes: [node1,node2]
#所有未分表的SQL,都会发往默认node。
default: node1
shard:
-
#分表使用的db
db : kingshard
#分表名字
table: test_shard_hash
#分表字段
key: id
#分表分布的node
nodes: [node1, node2]
#分表类型
type: hash
#子表个数分布,表示node1有4个子表,
#node2有4个子表。
locations: [4,4]
-
#分表使用的db
db : kingshard
#分表名字
table: test_shard_range
#分表字段
key: id
#分表类型
type: range
#分表分布的node
nodes: [node1, node2]
#子表个数分布,表示node1有4个子表,
#node2有4个子表。
locations: [4,4]
#表示每个子表包含的最大记录数,也就是说每
#个子表最多包好10000条记录。即子表1对应的id为[0,10000),子表2[10000,20000)....
table_row_limit: 10000
|
这里着重说一下分表的配置规则:
- kingshard支持两种类型的分表规则:hash和range。
- kingshard分表涉及到的子表,需要用户在各个db手动创建好,并且格式是:
table_name_%4d,也就是说子表下标由4位数组成。例如:table_name_0000,table_name_0102。
- 所有操作未分表的SQL语句都将发送到默认节点。
有关sharding设置是通过schema设置,一个kingshard实例只能有一个schemas,从上面的配置可以看出,schema可以分为三个部分:
-
db,表示这个schemas使用的数据库。
-
nodes,表示子表分布的节点名字。
-
rules,sharding规则。其中rules又可以分为两个部分:
- default,默认分表规则。所有操作不在shard(default规则下面的则)中的表的SQL语句都会发向该node。
- hash,hash分表方式。
- range,range分表方式
安装和启动
- 安装Go语言环境(请使用最新版),具体步骤请Google。
- git clone https://github.com/flike/kingshard.git src/github.com/flike/kingshard
- cd src/github.com/flike/kingshard
- source ./dev.sh
- make
- 设置配置文件
- 运行kingshard。./bin/kingshard -config=etc/ks.yaml
注意:
1. kingshard会响应SIGINT,SIGTERM,SIGQUIT这三个信号,平滑退出。在部署kingshard机器上应避免产生这三个信号,以免造成kingshard非正常退出!后台运行kingshard建议使用supervisor工具
2. kingshard采用的是yaml方式解析配置文件,需要注意的是yaml配置文件不允许出现tab键,且冒号后面需要跟一个空格。配置文件编写完成后,可以在yaml lint网站验证是否有格式错误。
3. 可以通过./bin/kingshard -v来查看kingshard的commit hash和编译时间,从而维持kingshard的版本。
4. etc目录下有两个配置文件(ks.yaml,unshard.yaml),如果需要分表功能,请基于ks.yaml修改配置。如果不需要分表,基于unshard.yaml修改配置。
跨节点分表
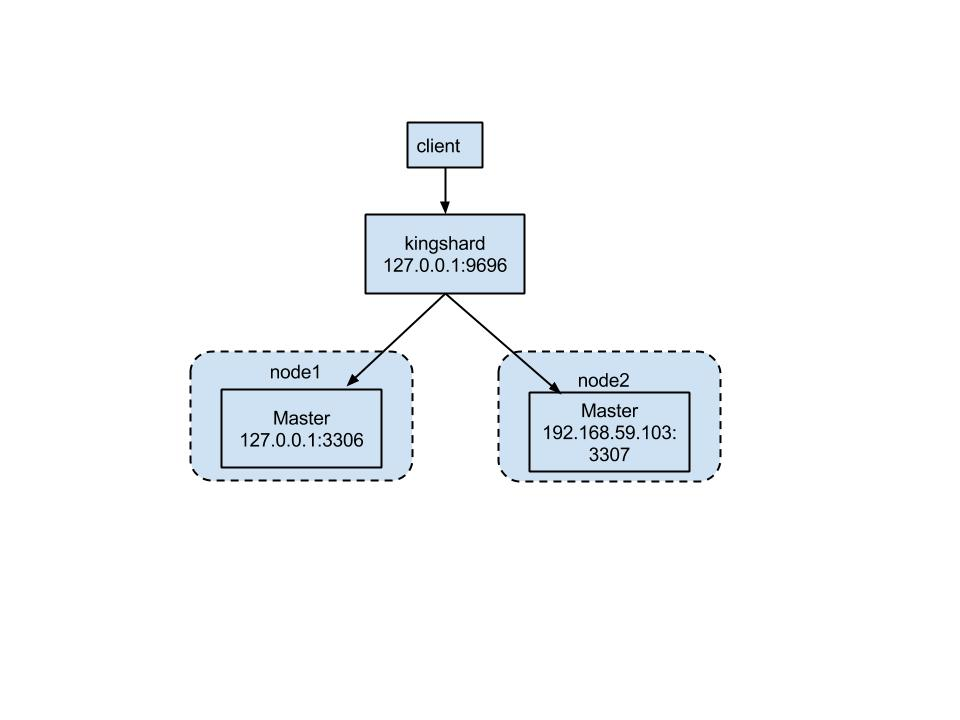
由于作者的只有两台MySQL,所以搭建了两个节点,这两个节点都只有一台Master 角色的MySQL数据库,具体的拓扑图如下所示:
分表操作演示
分表操作有hash和range两种类型,在这里只演示hash类型的分表操作,range类型的分表类似,就不再赘述了。
手动创建子表
在node1和node2上各创建4张子表,下面只给出在node1上test_shard_hash_0000的建表SQL语句,其他子表的建表SQL语句类似。node1包含:test_shard_hash_0000, test_shard_hash_0001, test_shard_hash_0002, test_shard_hash_0003。node2包含:test_shard_hash_0004, test_shard_hash_0005, test_shard_hash_0006, test_shard_hash_0007。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
CREATE TABLE `test_shard_hash_0000` (
`id` bigint(64) unsigned NOT NULL,
`str` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL,
`f` double DEFAULT NULL,
`e` enum('test1','test2') DEFAULT NULL,
`u` tinyint(3) unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
`i` tinyint(4) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
|
分表的插入和查询
执行下面SQL语句,根据查询的结果可以看出SQL语句根据分表规则落到不同的子表。查询操作(select)可以跨多个node,当更新操作涉及到多个node时,kingshard会以非事务的方式执行跨node的更新。为了保证数据一致性,请根据实际需求使用非事务方式的跨node更新操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
mysql> insert into test_shard_hash(id,str,f,e,u,i) values(15,"flike",3.14,'test2',2,3);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> mysql> insert into test_shard_hash(id,str,f,e,u,i) values(7,"chen",2.1,'test1',32,3);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into test_shard_hash(id,str,f,e,u,i) values(17,"github",2.5,'test1',32,3);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into test_shard_hash(id,str,f,e,u,i) values(18,"kingshard",7.3,'test1',32,3);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
|
对应的SQL日志如下所示:
1
2
3
4
|
2015/09/02 18:48:24 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->192.168.59.103:3307:insert into test_shard_hash_0007(id, str, f, e, u, i) values (15, 'flike', 3.14, 'test2', 2, 3)
2015/09/02 18:49:05 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->192.168.59.103:3307:insert into test_shard_hash_0007(id, str, f, e, u, i) values (7, 'chen', 2.1, 'test1', 32, 3)
2015/09/02 18:49:51 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->127.0.0.1:3306:insert into test_shard_hash_0001(id, str, f, e, u, i) values (17, 'github', 2.5, 'test1', 32, 3)
2015/09/02 18:50:21 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->127.0.0.1:3306:insert into test_shard_hash_0002(id, str, f, e, u, i) values (18, 'kingshard', 7.3, 'test1', 32, 3)
|
可以看到前两条SQL发送到了node2的master上了,后两条SQL发送到node1上的master了。
然后我们可以用select语句查看数据,且select支持跨node查询。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
mysql> select * from test_shard_hash where id < 18;
+----+--------+------+-------+------+------+
| id | str | f | e | u | i |
+----+--------+------+-------+------+------+
| 17 | github | 2.5 | test1 | 32 | 3 |
| 7 | chen | 2.1 | test1 | 32 | 3 |
| 15 | flike | 3.14 | test2 | 2 | 3 |
+----+--------+------+-------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.02 sec)
|
因为是hash类型的分表,所以对于select范围类型的查询,必须查询每一个子表。对应的SQL日志如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0000 where id < 18
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0001 where id < 18
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0002 where id < 18
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0003 where id < 18
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0004 where id < 18
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0005 where id < 18
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0006 where id < 18
2015/09/02 18:55:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0007 where id < 18
|
对应等值的select查询,kingshard会计算出具体命中的子表,然后只会在相应的子表中查询。对应的SQL如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
mysql> select * from test_shard_hash where id = 18;
+----+-----------+------+-------+------+------+
| id | str | f | e | u | i |
+----+-----------+------+-------+------+------+
| 18 | kingshard | 7.3 | test1 | 32 | 3 |
+----+-----------+------+-------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
对应的SQL日志如下所示:
1
|
2015/09/02 18:59:37 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0002 where id = 18
|
分表的更新
当更新的记录落在同一个子表时,kingshard支持这类操作。在上面插入的记录中,id为7和15的记录都落在test_shard_hash_0007中,所以可以成功地执行下面的SQL:
1
2
|
mysql> update test_shard_hash set u=123 where id = 15 or id = 7;
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)
|
对应的SQL日志是:
1
|
2015/09/02 19:17:27 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55003->192.168.59.103:3307:update test_shard_hash_0007 set u = 123 where id = 15 or id = 7
|
当更新的记录落在不同的子表,kingshard会以非事务的方式将更新操作发送到多个node上。例如执行如下SQL:
1
2
|
mysql> update test_shard_hash set str="myworld_test4" where id in(128,1,231);
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
|
对应的SQL日志是:
1
2
3
|
2016/03/15 15:18:27 - OK - 1.2ms - 127.0.0.1:60730->127.0.0.1:3306:update test_shard_hash_0000 set str = 'myworld_test4' where id in (128, 1, 231)
2016/03/15 15:18:27 - OK - 0.5ms - 127.0.0.1:60730->127.0.0.1:3306:update test_shard_hash_0001 set str = 'myworld_test4' where id in (128, 1, 231)
2016/03/15 15:18:27 - OK - 6.8ms - 127.0.0.1:60730->192.168.59.103:3307:update test_shard_hash_0007 set str = 'myworld_test4' where id in (128, 1, 231)
|
指定发送的node
有时候我们需要操作的表,不在default node中。在kingshard中允许用户将特定的sql路由到指定的node上。只需要在sql语句前面加上包含node名称的注释(连接MySQL时需要加上-c选项,避免客户端过滤掉注释)。例如:
1
|
mysql -h127.0.0.1 -ukingshard -pkingshard -P9696 -c;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
mysql> /*node2*/show tables;
+-----------------------+
| Tables_in_kingshard |
+-----------------------+
| kingshard_test_conn |
| test_shard_hash_0004 |
| test_shard_hash_0005 |
| test_shard_hash_0006 |
| test_shard_hash_0007 |
| test_shard_range_0004 |
| test_shard_range_0005 |
| test_shard_range_0006 |
| test_shard_range_0007 |
+-----------------------+
9 rows in set (0.03 sec)
mysql> /*node2*/select * from kingshard_test_conn;
Empty set (0.01 sec)
mysql> /*node2*/desc kingshard_test_conn;
+-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | bigint(20) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| str | varchar(256) | YES | | NULL | |
| f | double | YES | | NULL | |
| e | enum('test1','test2') | YES | | NULL | |
| u | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| i | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> /*node2*/insert into kingshard_test_conn values(10,"hello",10.2,'test1',1,1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> /*node2*/select * from kingshard_test_conn;
+----+-------+------+-------+------+------+
| id | str | f | e | u | i |
+----+-------+------+-------+------+------+
| 10 | hello | 10.2 | test1 | 1 | 1 |
+----+-------+------+-------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
强制读主库
有时候在主库中插入数据后,希望立即从主库读出来。在kingshard中由于读写分离的原因,select默认会发送到相应node的从库上。但是只需要在select语句中加入相应的注释项(/*master*/),就可以将select语句发送到主库。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
mysql> select/*master*/ * from kingshard_test_conn;
+----+----------+------+-------+------+------+
| id | str | f | e | u | i |
+----+----------+------+-------+------+------+
| 1 | a | 3.14 | test1 | NULL | NULL |
| 5 | ""''\abc | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 6 | 中国 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+----+----------+------+-------+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
|
跨node的sum和count函数
在kingshard中,支持sum和count函数,kingshard会将相应的SQL发送到正确的DB,并将结果合并起来再返回给客户的。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
mysql> select count(id) from test_shard_hash where id > 1;
+-----------+
| count(id) |
+-----------+
| 4 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
mysql> select sum(id) from test_shard_hash where id > 1;
+---------+
| sum(id) |
+---------+
| 57 |
+---------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
|
相应的SQL日志如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0000 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0001 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0002 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0003 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0004 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0005 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0006 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:01 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select count(id) from test_shard_hash_0007 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0000 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0001 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0002 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0003 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0004 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0005 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0006 where id > 1
2015/09/03 14:49:14 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select sum(id) from test_shard_hash_0007 where id > 1
|
跨node的order by
kingshard支持跨node的select操作使用order by,kingshard先将合适的SQL发生到对应的node,然后将结果集在内存中排序,从而实现select的order by操作。示例如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
mysql> select * from test_shard_hash where id > 1 order by id;
+----+-----------+------+-------+------+------+
| id | str | f | e | u | i |
+----+-----------+------+-------+------+------+
| 7 | chen | 2.1 | test1 | 123 | 3 |
| 15 | flike | 3.14 | test2 | 123 | 3 |
| 17 | github | 2.5 | test1 | 32 | 23 |
| 18 | kingshard | 7.3 | test1 | 32 | 23 |
+----+-----------+------+-------+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.02 sec)
|
对应的SQL日志为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0000 where id > 1 order by id asc
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0001 where id > 1 order by id asc
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0002 where id > 1 order by id asc
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_hash_0003 where id > 1 order by id asc
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0004 where id > 1 order by id asc
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0005 where id > 1 order by id asc
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0006 where id > 1 order by id asc
2015/09/03 14:54:11 - INFO - 127.0.0.1:55768->192.168.59.103:3307:select * from test_shard_hash_0007 where id > 1 order by id asc
|
单node的事务
kingshard支持在单个node上执行事务,也就是说同一个事务不能跨多个node,当出现跨node的情况时,kingshard会返回错误给客户端。可以跨同node上的不同子表。示例如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into test_shard_hash(id,str,f,e,u,i) values(23,'proxy',9.2,'test1',12,3);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
|
当在一个事务中,出现跨node的SQL语句时,kingshard会返回错误:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#SQL语句在node2中执行
mysql> insert into test_shard_hash(id,str,f,e,u,i) values(31,'proxy',9.2,'test1',12,3);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
#SQL语句在需要在node1执行,跨node了。
mysql> insert into test_shard_hash(id,str,f,e,u,i) values(40,'proxy',9.2,'test1',12,3);
ERROR 1105 (HY000): transaction in multi node
|
sharding
现在开源的MySQL Proxy已经有几款了,并且有的已经在生产环境上广泛应用。但这些proxy在sharding方面,都是不能分子表的。也就是说一个node节点只能分一张表。但我们的线上需求通常是这样的:
我有一张非常大的表,行数超过十亿,需要进行拆分处理。假设拆分因子是512。
如果采用单node单数据库的分表方式,那其实这512个子表还是存在一个物理节点上,意义不大。
如果采用他们的sharding功能,就需要512个物理节点,也不现实。
面对这种需求,现有的proxy就不能很好地满足要求了。通常我们希望将512张子表均分在几个MySQL节点上,从而达到系统的横向扩展。
然而kingshard较好地实现了这种典型的需求。简单来说,kingshard的分表方案采用两级映射的方式:
- kingshard将该表分成512张子表,例如:test_0000,test_0001,…test_0511。
- 将shardKey通过hash或range方式定位到其要操作的记录在哪张子表上。
- 子表落在哪个node上通过配置文件设置。
支持操作
目前kingshard sharding支持insert, delete, select, update和replace语句, 所有这五类操作都支持跨子表。但写操作的原子性仅支持单node上的跨子表,select操作则可以跨node,跨子表。
sharding方式
range方式
基于整数范围划分来得到子表下标。该方式的优点:基于范围的查询或更新速度快,因为查询(或更新)的范围有可能落在同一张子表中。这样可以避免全部子表的查询(更新)。缺点:数据热点问题。因为在一段时间内整个集群的写压力都会落在一张子表上。此时整个mysql集群的写能力受限于单台mysql server的性能。并且,当正在集中写的mysql 节点如果宕机的话,整个mysql集群处于不可写状态。基于range方式的分表字段类型受限。
hash方式
kingshard采用(shardKey%子表个数)的方式得到子表下标。优点:数据分布均匀,写压力会比较平均地落在后端的每个MySQL节点上,整个集群的写性能不会受限于单个MySQL节点。并且当某个分片节点宕机,只会影响到写入该节点的请求,其他节点的写入请求不受影响。分表字段类型不受限。因为任何一个类型的分表字段,都可以通过一个hash函数计算得到一个整数。缺点:基于范围的查询或更新,都需要将请求发送到全部子表,对性能有一定影响。但如果不是基于范围的查询或更新,则性能不会受到影响。
时间维度分表
按时间维度分表的场景非常普遍,下面介绍一下kingshard的时间分表功能
支持的时间类型
kingshard中的分表字段支持MySQL中三种类型的时间格式
- date类型,格式:YYYY-MM-DD,例如:2016-03-04,注意:2016-3-04,2016-03-4,2016-3-4等格式kingshard都是不支持的。
- datetime类型,格式:YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS,例如:2016-03-04 13:23:43,注意:2016-3-04 13:23:43,2016-03-4 13:23:43,2016-3-4 13:23:43等格式kingshard都是不支持的,必须严格按照规定的格式,kingshard才支持。
- timestamp类型,整数类型,例如:1457165568,对应的是:2016-3-5 16:12:48。
支持的时间分表类型
kingshard支持MySQL中三种格式的时间类型
- date类型,格式:YYYY-MM-DD,例如:2016-03-04,注意:2016-3-04,2016-03-4,2016-3-4等格式kingshard都是不支持的。
- datetime,格式:YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS,例如:2016-03-04 13:23:43,注意:2016-3-04 13:23:43,2016-03-4 13:23:43,2016-3-4 13:23:43等格式kingshard都是不支持的,必须严格按照规定的格式,kingshard才支持。
- timestamp,整数类型。
功能演示
kingshard的配置文件如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
schema_list :
-
user: kingshard
nodes: [node1,node2]
default: node1
shard:
-
db : kingshard
table: test_shard_year
key: ctime
type: date_year
nodes: [node1,node2]
date_range: [2015-2016,2017-2018]
|
按年分表
配置说明
按年分表的配置项设置如下:
1
2
3
4
5
|
table: test_shard_year
key: ctime
type: date_year
nodes: [node1,node2]
date_range: [2015-2016,2017-2018]
|
该配置表示:
- sharding key是ctime。
- 按年的分表类型是:
date_year。
test_shard_year_2015, test_shard_year_2016两个子表落在node1上,test_shard_year_2017,test_shard_year_2018两个子表落在node2上。- 如果你一个node上只包含一张子表,你可以这样配置
date_range[2015,2017-2018]。
注意:子表的命名格式必须是:shard_table_YYYY,shard_table是分表名,后面接具体的年。传入范围必须是有序递增的,不能是[2016,2013-2014]
功能演示
在node1上创建两张子表test_shard_year_2015, test_shard_year_2016,在node2上创建两种子表test_shard_year_2017,test_shard_year_2018。建表SQL如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
CREATE TABLE `test_shard_year_2016` (
`id` int(10) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`ctime` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
|
插入数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
mysql> insert into test_shard_year(id,name,ctime) values(12,"hello","2015-02-22 13:23:45");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into test_shard_year(id,name,ctime) values(13,"world","2016-03-22");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_shard_year where ctime < "2016-03-23";
+----+-------+---------------------+
| id | name | ctime |
+----+-------+---------------------+
| 12 | hello | 2015-02-22 13:23:45 |
| 13 | world | 2016-03-22 00:00:00 |
+----+-------+---------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
对应的SQL log信息是:
1
2
3
4
|
2016/03/05 12:06:32 - OK - 1.2ms - 127.0.0.1:56597->127.0.0.1:3306:insert into test_shard_year_2015(id, name, ctime) values (12, 'hello', '2015-02-22 13:23:45')
2016/03/05 12:06:59 - OK - 2.0ms - 127.0.0.1:56597->127.0.0.1:3306:insert into test_shard_year_2016(id, name, ctime) values (13, 'world', '2016-03-22')
2016/03/05 12:08:30 - OK - 1.6ms - 127.0.0.1:56597->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_year_2015 where ctime < '2016-03-23'
2016/03/05 12:08:30 - OK - 0.3ms - 127.0.0.1:56597->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_year_2016 where ctime < '2016-03-23'
|
当然如果你把id作为一个unix时间戳,来分表的话,kingshard也是支持的。具体配置就是这样的:
1
2
3
4
5
|
table: test_shard_year
key: id
type: date_year
nodes: [node1,node2]
date_range: [2015-2016,2017-2018]
|
插入数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
mysql> insert into test_shard_year(id,name,ctime) values(1457410310,"world","2018-03-22");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from test_shard_year where id = 1457410310;
+------------+-------+---------------------+
| id | name | ctime |
+------------+-------+---------------------+
| 1457410310 | world | 2018-03-22 00:00:00 |
+------------+-------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
1457410310 这个unix时间戳对应的日期是:2016-3-8 12:11:50。kingshard准确地将这条记录路由到了test_shard_year_2016这张子表中了。
对应的SQL log是:
1
2
|
2016/03/08 12:12:49 - OK - 1.0ms - 127.0.0.1:56669->127.0.0.1:3306:insert into test_shard_year_2016(id, name, ctime) values (1457410310, 'world', '2018-03-22')
2016/03/08 12:13:23 - OK - 0.4ms - 127.0.0.1:56669->127.0.0.1:3306:select * from test_shard_year_2016 where id = 1457410310
|
按月分表
配置说明
按月分表的配置项设置如下:
1
2
3
4
5
|
table: test_shard_month
key: ctime
type: date_month
nodes: [node1,node2]
date_range: [201512-201602,201609-2016010]
|
该配置表示:
- sharding key是ctime。
- 按月的分表类型是:
date_month。
test_shard_month_201512, test_shard_month_201601, test_shard_month_201602两个子表落在node1上,test_shard_month_201609,test_shard_month_201610两个子表落在node2上。- 如果你一个node上只包含一张子表,你可以这样配置
date_range[201501,201609-201610]。
注意:子表的命名格式必须是:shard_table_YYYYMM,shard_table是分表名,后面接具体的年和月。传入范围必须是有序递增的,不能是[201609-201610,201501]
功能演示参考按年分表的操作。
按天分表
配置说明
按天分表的配置项设置如下:
1
2
3
4
5
|
table: test_shard_day
key: ctime
type: date_day
nodes: [node1,node2]
date_range: [20151222-20151224,20160901-20160902]
|
该配置表示:
- sharding key是ctime。
- 按天的分表类型是:
date_day。
test_shard_day_20151222, test_shard_day_20151223, test_shard_day_20151224两个子表落在node1上,test_shard_day_20160901,test_shard_day_20160902两个子表落在node2上。- 如果你一个node上只包含一张子表,你可以这样配置
date_range[20150101,20160901-20161010]。
注意:子表的命名格式必须是:shard_table_YYYYMMDD,shard_table是分表名,后面接具体的年,月和日。传入范围必须是有序递增的,不能是[20160901-20161010,20150101]
功能演示参考按年分表的操作。
子表迁移方案
通过kingshard可以非常方便地动态迁移子表,从而保证MySQL节点的不至于负载压力太大。大致步骤如下所述:
- 通过自动数据迁移工具开始数据迁移。
- 数据差异小于某一临界值,阻塞老子表写操作(read-only)
- 等待新子表数据同步完毕
- 更改kingshard配置文件中的对应子表的路由规则。
- 删除老节点上的子表。
Kingshard支持SQL的范围
简要说明
kingshard在非分表的情况下支持绝大部分MySQL语法和协议,包括类似SHOW DATABASES, SHOW TABLES, 以及各种DML语句和DDL语句。在分表的情况下,目前只支持有限的DML语句,主要包含:SELECT,UPDATE,INSERT,REPLACE, DELETE这五种SQL操作。并且不支持自动建子表功能。以及有限的kingshard自定义管理端命令。在分表和非分表的情况下,都不支持以下情形:
- 暂不支持用户自定义数据类型、自定义函数。
- 暂不支持视图、存储过程、触发器、游标。
- 暂不支持类似 BEGIN…END,LOOP…END LOOP,REPEAT…UNTIL…END REPEAT,WHILE…DO…END WHILE 等的复合语句。
- 暂不支类似 IF,WHILE 等流程控制类语句。
下面分两部分介绍kingshard支持SQL的情况:非分表情况下SQL支持范围和分表情况下SQL支持范围。
非分表情况下SQL的支持范围
以下说明都是基于非分表的情况下,SQL的支持情况。
数据库DDL语法
- CREATE TABLE Syntax
- CREATE INDEX Syntax
- DROP TABLE Syntax
- DROP INDEX Syntax
- ALTER TABLE Syntax
- TRUNCATE TABLE Syntax
数据库DML语法
- INSERT Syntax
- INSERT DELAYED Syntax 暂不支持
- REPLACE Syntax
- UPDATE Syntax
- DELETE Syntax
- Subquery Syntax
- Scalar Subquery
- Comparisons Subquery
- Subqueries with ANY, IN, or SOME
- Subqueries with ALL
- Row Subqueries
- Subqueries with EXISTS or NOT EXISTS
- Subqueries in the FROM Clause
- SELECT Syntax
- SELECT INTO OUTFILE/INTO DUMPFILE/INTO var_name 暂不支持
- Last_insert_id特性
事务的支持
- START TRANSACTION, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK Syntax
- 暂不支持transaction_characteristic定义
- 暂不支持savepoint嵌套事务的相关语法
- 暂不支持XA事务的相关语法
- 支持set autocommit=0/1方式设置事务.
- 支持begin/commit方式设置事务
- 支持start transaction方式设置事务
- SET TRANSACTION Syntax
- 暂不支持对global的事务隔离级别进行调整
预处理的支持
支持主流语言(java,php,python,C/C++,Go)SDK的MySQL的Prepare语法。
数据库管理语法的支持
- SET Syntax
只支持字符集和set autocommit相关语法,其他set语法未测试过。
- Show Syntax
默认show操作会转发到默认DB,需要查看其他DB的内容,通过在SQL中加注释的方式。
- KILL Syntax
目前不支持KILL QUERY processlist_id
数据库管理语法的支持
- DESCRIBE Syntax
- EXPLAIN Syntax
- USE Syntax
数据库系统函数的支持
默认都支持(未测试)
分表的情况下SQL的支持范围
数据库DDL语法
- CREATE TABLE Syntax
- CREATE INDEX Syntax
- DROP TABLE Syntax
- DROP INDEX Syntax
- ALTER TABLE Syntax
- TRUNCATE TABLE Syntax
分表的情况下支持这些语法,但需要在SQL中加注释,例如:
/*node1*/create table stu_0000(id int, name char(20));
这样kingshard就会将该SQL转发到node1节点的Master上。
注:
truncate如果不指定节点注释则会将所有分表都清空,例如:truncate stu
数据库DML语法
- INSERT Syntax
- INSERT DELAYED Syntax 不支持
- INSERT INTO SELECT 不支持
- REPLACE Syntax
- UPDATE Syntax
//分表使用的字段无论何种分表类型都不能作为被更新的字段。
- UPDATE SET xx=REPLACE(xx,‘a’,‘b’) Syntax 不支持
- DELETE Syntax
- Subquery Syntax
- SELECT Syntax
对于UPDATE,DELETE和SELECT三种SQL中WHERE后面的条件不能包含子查询,函数等。只能是字段名。
数据库管理语法的支持
- DESCRIBE Syntax
通过SQL语句hint方式支持,例如:
/*node2*/describe table_name
- EXPLAIN Syntax
通过SQL语句hint方式支持,例如:
/*node2*/explain select * from xxxx
- USE Syntax
分表聚合函数的支持
支持以下聚合函数:
- sum函数
- max函数
- count函数
- min函数
不支持distinct后聚合,例如:
select count(distinct id) from xxxx
分表group by,order by,limit支持
支持分表情况下的group by, order by, limit
其他情形说明
- 不支持分布式事务,支持以非事务的方式更新多node上的数据。
- 不支持预处理。
- 不支持数据库管理语法。
转载:https://github.com/flike/kingshard/blob/master/README_ZH.md

