1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
|
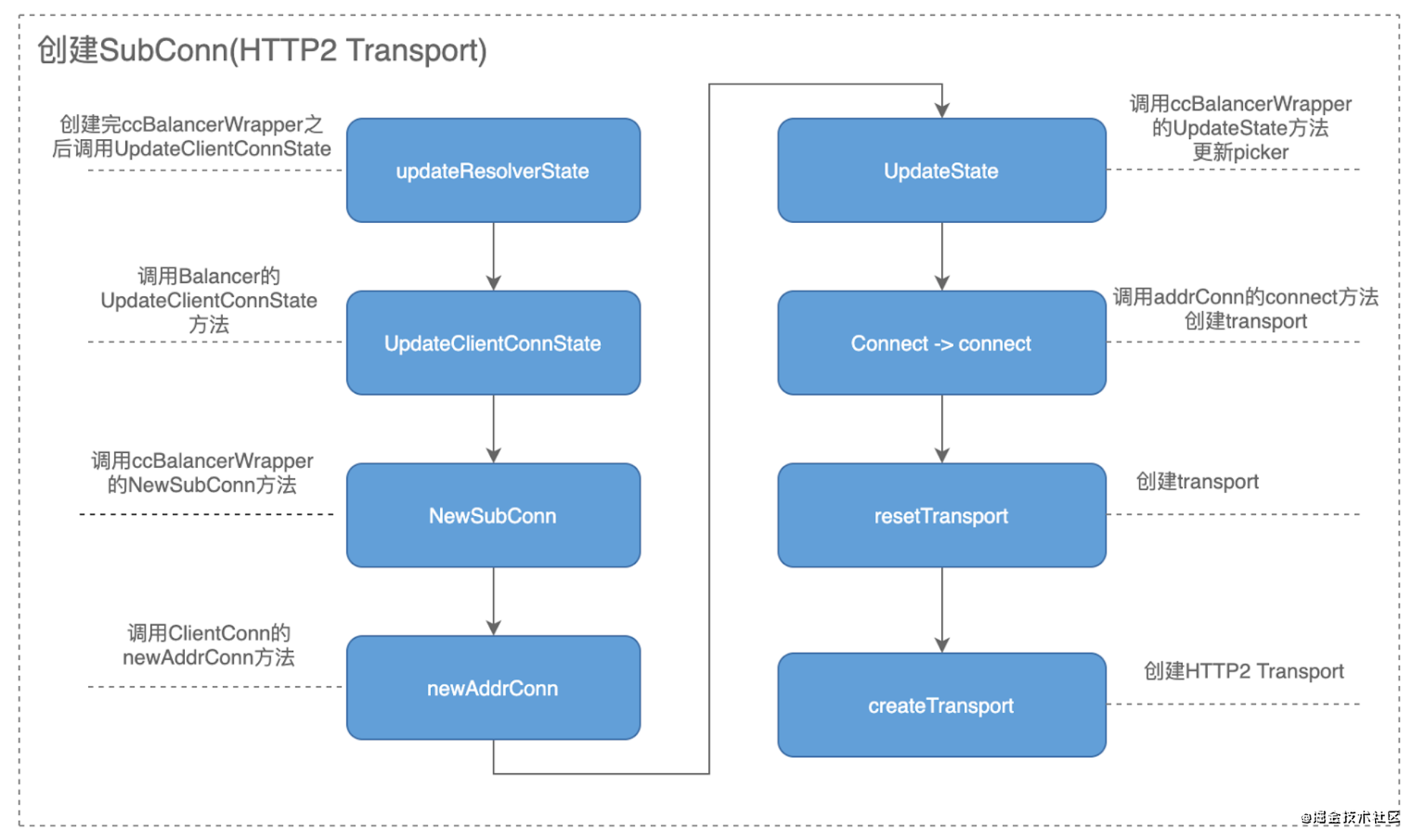
// addrConn is a network connection to a given address.
type addrConn struct {
//首先是 ctx 和 cancel 两个字段,它与 clientConn 的 ctx、cancel 相同,大体上 go 中各种 Conn 结构体都携带着这两个字段。
ctx context.Context
cancel context.CancelFunc
//cc 指向 ClientConn 的引用,dopts、scopts 是原始的参数。
cc *ClientConn
dopts dialOptions
//acbw 是另一个 wrapper 对象,acBalancerWrapper,它是 SubConn 接口的实现,方法有 UpdateAddresses 和 Connect。balancer 也可以通过 SubConn 接口来更新每个 SubConn 的地址列表。
//SubConn 在定义上是对应多个地址,取这些地址中的首个可连接的地址建立连接。猜可能是为了比较高级的负载均衡策略而准备的,比如将后端实例分组,对组做负载均衡,组内做 Active/Standby 的模式。
acbw balancer.SubConn
scopts balancer.NewSubConnOptions
// transport is set when there's a viable transport (note: ac state may not be READY as LB channel
// health checking may require server to report healthy to set ac to READY), and is reset
// to nil when the current transport should no longer be used to create a stream (e.g. after GoAway
// is received, transport is closed, ac has been torn down).
transport transport.ClientTransport // The current transport.
mu sync.Mutex
//curAddr、addrs 表示 addrConn 的地址列表和当前地址。state 表示连接状态,这些都比较好理解。
curAddr resolver.Address // The current address.
addrs []resolver.Address // All addresses that the resolver resolved to.
// Use updateConnectivityState for updating addrConn's connectivity state.
state connectivity.State
backoffIdx int // Needs to be stateful for resetConnectBackoff.
resetBackoff chan struct{}
channelzID int64 // channelz unique identification number.
czData *channelzData
}
// connect starts creating a transport.
// It does nothing if the ac is not IDLE.
// TODO(bar) Move this to the addrConn section.
//balancer 发起的 Connect,最终调用到 addrConn 的 connect 方法:
func (ac *addrConn) connect() error {
ac.mu.Lock()
//如果处于 Shutdown 则直接退出返回 errConnClosing,如果并非 IDLE 状态,则什么都不做,直接退出也不返回错误。
if ac.state == connectivity.Shutdown {
ac.mu.Unlock()
return errConnClosing
}
if ac.state != connectivity.Idle {
ac.mu.Unlock()
return nil
}
// Update connectivity state within the lock to prevent subsequent or
// concurrent calls from resetting the transport more than once.
// 将 connectivityState 设置为 Connecting
ac.updateConnectivityState(connectivity.Connecting, nil)
ac.mu.Unlock()
// Start a goroutine connecting to the server asynchronously.
//然后开一个 goroutine 异步连接到服务端。
go ac.resetTransport()
return nil
}
// tryUpdateAddrs tries to update ac.addrs with the new addresses list.
//
// If ac is Connecting, it returns false. The caller should tear down the ac and
// create a new one. Note that the backoff will be reset when this happens.
//
// If ac is TransientFailure, it updates ac.addrs and returns true. The updated
// addresses will be picked up by retry in the next iteration after backoff.
//
// If ac is Shutdown or Idle, it updates ac.addrs and returns true.
//
// If ac is Ready, it checks whether current connected address of ac is in the
// new addrs list.
// - If true, it updates ac.addrs and returns true. The ac will keep using
// the existing connection.
// - If false, it does nothing and returns false.
func (ac *addrConn) tryUpdateAddrs(addrs []resolver.Address) bool {
ac.mu.Lock()
defer ac.mu.Unlock()
channelz.Infof(logger, ac.channelzID, "addrConn: tryUpdateAddrs curAddr: %v, addrs: %v", ac.curAddr, addrs)
if ac.state == connectivity.Shutdown ||
ac.state == connectivity.TransientFailure ||
ac.state == connectivity.Idle {
ac.addrs = addrs
return true
}
if ac.state == connectivity.Connecting {
return false
}
// ac.state is Ready, try to find the connected address.
var curAddrFound bool
for _, a := range addrs {
if reflect.DeepEqual(ac.curAddr, a) {
curAddrFound = true
break
}
}
channelz.Infof(logger, ac.channelzID, "addrConn: tryUpdateAddrs curAddrFound: %v", curAddrFound)
if curAddrFound {
ac.addrs = addrs
}
return curAddrFound
}
// Note: this requires a lock on ac.mu.
func (ac *addrConn) updateConnectivityState(s connectivity.State, lastErr error) {
if ac.state == s {
return
}
ac.state = s
channelz.Infof(logger, ac.channelzID, "Subchannel Connectivity change to %v", s)
ac.cc.handleSubConnStateChange(ac.acbw, s, lastErr)
}
// adjustParams updates parameters used to create transports upon
// receiving a GoAway.
func (ac *addrConn) adjustParams(r transport.GoAwayReason) {
switch r {
case transport.GoAwayTooManyPings:
v := 2 * ac.dopts.copts.KeepaliveParams.Time
ac.cc.mu.Lock()
if v > ac.cc.mkp.Time {
ac.cc.mkp.Time = v
}
ac.cc.mu.Unlock()
}
}
// resetTransport 主要内容就是一个for 循环,可以看到在这个for循环中会尝试建立链接。如果建立成功就返回一个nil。如果不成功会不断重试下去。实际上不管是开头的Dial或者Dial完了关闭服务器后都是由这段代码来建立真实的链接。这也就是如果你使用withBlock 但是不使用超时的话会不断的重试下去。中途断掉也会不断重联。当然了重连的过程中是使用了backoff算法来重连。而且默认会在grpc的配置中有个默认最大重试间隔时间。默认是120.
// 1. 当连接失败后会等待一段时间之后再尝试重连,时间间隔的算法依赖于backoff.Strategy接口的Backoff方法.
// 2. 利用context的超时控制或取消机制,直接结束.
func (ac *addrConn) resetTransport() {
//进入循环
for i := 0; ; i++ {
//如果属于重试,则触发名字解析;
if i > 0 {
ac.cc.resolveNow(resolver.ResolveNowOptions{})
}
//对 ac 上锁:
ac.mu.Lock()
//如果 ac 目前属于 Shutdown 状态则直接退出
if ac.state == connectivity.Shutdown {
ac.mu.Unlock()
return
}
//根据重试次数计算退避时间和连接超时时间,重试次数越长,连接超时时间也越长;
addrs := ac.addrs
backoffFor := ac.dopts.bs.Backoff(ac.backoffIdx)
// This will be the duration that dial gets to finish.
// 超时时间,默认20秒.
dialDuration := minConnectTimeout
if ac.dopts.minConnectTimeout != nil {
dialDuration = ac.dopts.minConnectTimeout()
}
if dialDuration < backoffFor {
// Give dial more time as we keep failing to connect.
dialDuration = backoffFor
}
// We can potentially spend all the time trying the first address, and
// if the server accepts the connection and then hangs, the following
// addresses will never be tried.
//
// The spec doesn't mention what should be done for multiple addresses.
// https://github.com/grpc/grpc/blob/master/doc/connection-backoff.md#proposed-backoff-algorithm
connectDeadline := time.Now().Add(dialDuration)
//设置状态为 Connecting;
ac.updateConnectivityState(connectivity.Connecting, nil)
ac.transport = nil
//解锁
ac.mu.Unlock()
//调用 ac.tryAllAddrs(),按顺序尝试建立连接;
newTr, addr, reconnect, err := ac.tryAllAddrs(addrs, connectDeadline)
if err != nil {
// After exhausting all addresses, the addrConn enters
// TRANSIENT_FAILURE.
ac.mu.Lock()
// 如果失败了,且状态为Shutdown直接返回.
if ac.state == connectivity.Shutdown {
ac.mu.Unlock()
return
}
//如果失败,将状态置为 TransientFailure;
ac.updateConnectivityState(connectivity.TransientFailure, err)
// Backoff.
//按前面计算出的时间进行退避;
b := ac.resetBackoff
ac.mu.Unlock()
// 根据backoff时间创建定时器.
timer := time.NewTimer(backoffFor)
select {
case <-timer.C:
// backoff时间到,增加backoff次数,继续循环去尝试连接.
ac.mu.Lock()
ac.backoffIdx++
ac.mu.Unlock()
case <-b:
// 外部重置了backoff,马上重新循环去尝试连接.
timer.Stop()
case <-ac.ctx.Done():
// context取消了或超时了,直接返回.
timer.Stop()
return
}
continue
}
//调用 ac.tryAllAddrs() 成功,可得到 Transport 对象 newTr、addr 地址:
//对 ac 重新上锁:
ac.mu.Lock()
//如果属于 Shutdown 状态则直接退出;
if ac.state == connectivity.Shutdown {
ac.mu.Unlock()
newTr.Close()
return
}
//将 tryAllAddrs 得到的 addr 与 newTr 对象赋值给 ac 的 curAddr 字段和 transport 字段;
ac.curAddr = addr
ac.transport = newTr
ac.backoffIdx = 0
hctx, hcancel := context.WithCancel(ac.ctx)
//调用 ac.startHealthCheck 启动健康检查的 goroutine,为健康检查单开一个 context;
ac.startHealthCheck(hctx)
//解锁;
ac.mu.Unlock()
// Block until the created transport is down. And when this happens,
// we restart from the top of the addr list.
//等待 <-reconnect.Done(),关闭健康检查的 goroutine,重新进入循环;
<-reconnect.Done()
hcancel()
// restart connecting - the top of the loop will set state to
// CONNECTING. This is against the current connectivity semantics doc,
// however it allows for graceful behavior for RPCs not yet dispatched
// - unfortunate timing would otherwise lead to the RPC failing even
// though the TRANSIENT_FAILURE state (called for by the doc) would be
// instantaneous.
//
// Ideally we should transition to Idle here and block until there is
// RPC activity that leads to the balancer requesting a reconnect of
// the associated SubConn.
}
}
// tryAllAddrs tries to creates a connection to the addresses, and stop when at the
// first successful one. It returns the transport, the address and a Event in
// the successful case. The Event fires when the returned transport disconnects.
// tryAllAddrs 似乎主要是循环 addrs 列表,调用 ac.createTransport,连接如果失败则调用 blockingpicker.updateConnectionError(err) 将错误信息记录在 blockingpicker 里。到上层 ClientConn 发现连接失败时,都从 blockingpicker.connectionErr() 这里拿错误信息。
func (ac *addrConn) tryAllAddrs(addrs []resolver.Address, connectDeadline time.Time) (transport.ClientTransport, resolver.Address, *grpcsync.Event, error) {
var firstConnErr error
for _, addr := range addrs {
ac.mu.Lock()
if ac.state == connectivity.Shutdown {
ac.mu.Unlock()
return nil, resolver.Address{}, nil, errConnClosing
}
ac.cc.mu.RLock()
ac.dopts.copts.KeepaliveParams = ac.cc.mkp
ac.cc.mu.RUnlock()
copts := ac.dopts.copts
if ac.scopts.CredsBundle != nil {
copts.CredsBundle = ac.scopts.CredsBundle
}
ac.mu.Unlock()
channelz.Infof(logger, ac.channelzID, "Subchannel picks a new address %q to connect", addr.Addr)
newTr, reconnect, err := ac.createTransport(addr, copts, connectDeadline)
if err == nil {
return newTr, addr, reconnect, nil
}
if firstConnErr == nil {
firstConnErr = err
}
ac.cc.updateConnectionError(err)
}
// Couldn't connect to any address.
return nil, resolver.Address{}, nil, firstConnErr
}
//里面比较显眼的是几个回调:
//* onGoAway:GoAway 消息时候,将 Ready 状态置为 Connecting 状态,阻止该连接继续发请求出去;GoAway 消息该是 grpc 服务端的 graceful shutdown 流程;
//* onClose:处理流程同 onGoAway,将 Ready 状态置为 Connecting 状态,阻止该连接继续发请求出去,这里与 onGoaway 的处理共享同一个 once,相比 onGoAway 的区别是 onClose 多一个 close(onCloseCalled);
//* onPrefaceReceipt:执行 close(prefaceReceived) ,似乎表示收到 preface 消息,即连接成功建立的标识;好像有很多场景都使用 close(channel) 起到信号通知的作用。
//建立连接等待期间,transport 有可能被 Close 掉,这时会返回 errors.New("connection closed")。
// createTransport creates a connection to addr. It returns the transport and a
// Event in the successful case. The Event fires when the returned transport
// disconnects.
func (ac *addrConn) createTransport(addr resolver.Address, copts transport.ConnectOptions, connectDeadline time.Time) (transport.ClientTransport, *grpcsync.Event, error) {
prefaceReceived := make(chan struct{})
onCloseCalled := make(chan struct{})
reconnect := grpcsync.NewEvent()
// addr.ServerName takes precedent over ClientConn authority, if present.
if addr.ServerName == "" {
addr.ServerName = ac.cc.authority
}
once := sync.Once{}
onGoAway := func(r transport.GoAwayReason) {
ac.mu.Lock()
ac.adjustParams(r)
once.Do(func() {
if ac.state == connectivity.Ready {
// Prevent this SubConn from being used for new RPCs by setting its
// state to Connecting.
//
// TODO: this should be Idle when grpc-go properly supports it.
ac.updateConnectivityState(connectivity.Connecting, nil)
}
})
ac.mu.Unlock()
reconnect.Fire()
}
onClose := func() {
ac.mu.Lock()
once.Do(func() {
if ac.state == connectivity.Ready {
// Prevent this SubConn from being used for new RPCs by setting its
// state to Connecting.
//
// TODO: this should be Idle when grpc-go properly supports it.
ac.updateConnectivityState(connectivity.Connecting, nil)
}
})
ac.mu.Unlock()
close(onCloseCalled)
reconnect.Fire()
}
onPrefaceReceipt := func() {
close(prefaceReceived)
}
connectCtx, cancel := context.WithDeadline(ac.ctx, connectDeadline)
defer cancel()
if channelz.IsOn() {
copts.ChannelzParentID = ac.channelzID
}
newTr, err := transport.NewClientTransport(connectCtx, ac.cc.ctx, addr, copts, onPrefaceReceipt, onGoAway, onClose)
if err != nil {
// newTr is either nil, or closed.
channelz.Warningf(logger, ac.channelzID, "grpc: addrConn.createTransport failed to connect to %v. Err: %v. Reconnecting...", addr, err)
return nil, nil, err
}
select {
case <-time.After(time.Until(connectDeadline)):
// We didn't get the preface in time.
newTr.Close()
channelz.Warningf(logger, ac.channelzID, "grpc: addrConn.createTransport failed to connect to %v: didn't receive server preface in time. Reconnecting...", addr)
return nil, nil, errors.New("timed out waiting for server handshake")
case <-prefaceReceived:
// We got the preface - huzzah! things are good.
case <-onCloseCalled:
// The transport has already closed - noop.
return nil, nil, errors.New("connection closed")
// TODO(deklerk) this should bail on ac.ctx.Done(). Add a test and fix.
}
return newTr, reconnect, nil
}
// startHealthCheck starts the health checking stream (RPC) to watch the health
// stats of this connection if health checking is requested and configured.
//
// LB channel health checking is enabled when all requirements below are met:
// 1. it is not disabled by the user with the WithDisableHealthCheck DialOption
// 2. internal.HealthCheckFunc is set by importing the grpc/health package
// 3. a service config with non-empty healthCheckConfig field is provided
// 4. the load balancer requests it
//
// It sets addrConn to READY if the health checking stream is not started.
//
// Caller must hold ac.mu.
func (ac *addrConn) startHealthCheck(ctx context.Context) {
var healthcheckManagingState bool
defer func() {
if !healthcheckManagingState {
ac.updateConnectivityState(connectivity.Ready, nil)
}
}()
if ac.cc.dopts.disableHealthCheck {
return
}
healthCheckConfig := ac.cc.healthCheckConfig()
if healthCheckConfig == nil {
return
}
if !ac.scopts.HealthCheckEnabled {
return
}
healthCheckFunc := ac.cc.dopts.healthCheckFunc
if healthCheckFunc == nil {
// The health package is not imported to set health check function.
//
// TODO: add a link to the health check doc in the error message.
channelz.Error(logger, ac.channelzID, "Health check is requested but health check function is not set.")
return
}
healthcheckManagingState = true
// Set up the health check helper functions.
currentTr := ac.transport
newStream := func(method string) (interface{}, error) {
ac.mu.Lock()
if ac.transport != currentTr {
ac.mu.Unlock()
return nil, status.Error(codes.Canceled, "the provided transport is no longer valid to use")
}
ac.mu.Unlock()
return newNonRetryClientStream(ctx, &StreamDesc{ServerStreams: true}, method, currentTr, ac)
}
setConnectivityState := func(s connectivity.State, lastErr error) {
ac.mu.Lock()
defer ac.mu.Unlock()
if ac.transport != currentTr {
return
}
ac.updateConnectivityState(s, lastErr)
}
// Start the health checking stream.
go func() {
err := ac.cc.dopts.healthCheckFunc(ctx, newStream, setConnectivityState, healthCheckConfig.ServiceName)
if err != nil {
if status.Code(err) == codes.Unimplemented {
channelz.Error(logger, ac.channelzID, "Subchannel health check is unimplemented at server side, thus health check is disabled")
} else {
channelz.Errorf(logger, ac.channelzID, "HealthCheckFunc exits with unexpected error %v", err)
}
}
}()
}
func (ac *addrConn) resetConnectBackoff() {
ac.mu.Lock()
close(ac.resetBackoff)
ac.backoffIdx = 0
ac.resetBackoff = make(chan struct{})
ac.mu.Unlock()
}
// getReadyTransport returns the transport if ac's state is READY.
// Otherwise it returns nil, false.
// If ac's state is IDLE, it will trigger ac to connect.
func (ac *addrConn) getReadyTransport() (transport.ClientTransport, bool) {
ac.mu.Lock()
if ac.state == connectivity.Ready && ac.transport != nil {
t := ac.transport
ac.mu.Unlock()
return t, true
}
var idle bool
if ac.state == connectivity.Idle {
idle = true
}
ac.mu.Unlock()
// Trigger idle ac to connect.
if idle {
ac.connect()
}
return nil, false
}
//tearDown 调用的时机,一是在 balancerWrapper 的 UpdateAddresses,二是在 clientConn 的 removeAddr 和 Close()。参数有细微差异:
//* 在 Close() 时,传递 ErrClientConnClosing
//* 在 removeAddr() 和 UpdateAddresses() 时,传递 errConnDrain
//errConnDrain 表示是正常退出流程,会走 transport 对象的 GracefulClose 方法,而 ErrClientConnClosing 是类似于强杀的退出。里面有个细节是 GracefulClose 会回调 onClose,onClose() 里面又需要 ac 的 mu 这把锁,为此需要 GracefulClose 前先释放掉锁。
// tearDown starts to tear down the addrConn.
// TODO(zhaoq): Make this synchronous to avoid unbounded memory consumption in
// some edge cases (e.g., the caller opens and closes many addrConn's in a
// tight loop.
// tearDown doesn't remove ac from ac.cc.conns.
func (ac *addrConn) tearDown(err error) {
ac.mu.Lock()
if ac.state == connectivity.Shutdown {
ac.mu.Unlock()
return
}
curTr := ac.transport
ac.transport = nil
// We have to set the state to Shutdown before anything else to prevent races
// between setting the state and logic that waits on context cancellation / etc.
ac.updateConnectivityState(connectivity.Shutdown, nil)
ac.cancel()
ac.curAddr = resolver.Address{}
if err == errConnDrain && curTr != nil {
// GracefulClose(...) may be executed multiple times when
// i) receiving multiple GoAway frames from the server; or
// ii) there are concurrent name resolver/Balancer triggered
// address removal and GoAway.
// We have to unlock and re-lock here because GracefulClose => Close => onClose, which requires locking ac.mu.
ac.mu.Unlock()
curTr.GracefulClose()
ac.mu.Lock()
}
if channelz.IsOn() {
channelz.AddTraceEvent(logger, ac.channelzID, 0, &channelz.TraceEventDesc{
Desc: "Subchannel Deleted",
Severity: channelz.CtInfo,
Parent: &channelz.TraceEventDesc{
Desc: fmt.Sprintf("Subchanel(id:%d) deleted", ac.channelzID),
Severity: channelz.CtInfo,
},
})
// TraceEvent needs to be called before RemoveEntry, as TraceEvent may add trace reference to
// the entity being deleted, and thus prevent it from being deleted right away.
channelz.RemoveEntry(ac.channelzID)
}
ac.mu.Unlock()
}
func (ac *addrConn) getState() connectivity.State {
ac.mu.Lock()
defer ac.mu.Unlock()
return ac.state
}
func (ac *addrConn) ChannelzMetric() *channelz.ChannelInternalMetric {
ac.mu.Lock()
addr := ac.curAddr.Addr
ac.mu.Unlock()
return &channelz.ChannelInternalMetric{
State: ac.getState(),
Target: addr,
CallsStarted: atomic.LoadInt64(&ac.czData.callsStarted),
CallsSucceeded: atomic.LoadInt64(&ac.czData.callsSucceeded),
CallsFailed: atomic.LoadInt64(&ac.czData.callsFailed),
LastCallStartedTimestamp: time.Unix(0, atomic.LoadInt64(&ac.czData.lastCallStartedTime)),
}
}
func (ac *addrConn) incrCallsStarted() {
atomic.AddInt64(&ac.czData.callsStarted, 1)
atomic.StoreInt64(&ac.czData.lastCallStartedTime, time.Now().UnixNano())
}
func (ac *addrConn) incrCallsSucceeded() {
atomic.AddInt64(&ac.czData.callsSucceeded, 1)
}
func (ac *addrConn) incrCallsFailed() {
atomic.AddInt64(&ac.czData.callsFailed, 1)
}
type retryThrottler struct {
max float64
thresh float64
ratio float64
mu sync.Mutex
tokens float64 // TODO(dfawley): replace with atomic and remove lock.
}
// throttle subtracts a retry token from the pool and returns whether a retry
// should be throttled (disallowed) based upon the retry throttling policy in
// the service config.
func (rt *retryThrottler) throttle() bool {
if rt == nil {
return false
}
rt.mu.Lock()
defer rt.mu.Unlock()
rt.tokens--
if rt.tokens < 0 {
rt.tokens = 0
}
return rt.tokens <= rt.thresh
}
func (rt *retryThrottler) successfulRPC() {
if rt == nil {
return
}
rt.mu.Lock()
defer rt.mu.Unlock()
rt.tokens += rt.ratio
if rt.tokens > rt.max {
rt.tokens = rt.max
}
}
type channelzChannel struct {
cc *ClientConn
}
func (c *channelzChannel) ChannelzMetric() *channelz.ChannelInternalMetric {
return c.cc.channelzMetric()
}
// ErrClientConnTimeout indicates that the ClientConn cannot establish the
// underlying connections within the specified timeout.
//
// Deprecated: This error is never returned by grpc and should not be
// referenced by users.
var ErrClientConnTimeout = errors.New("grpc: timed out when dialing")
func (cc *ClientConn) getResolver(scheme string) resolver.Builder {
for _, rb := range cc.dopts.resolvers {
if scheme == rb.Scheme() {
return rb
}
}
return resolver.Get(scheme)
}
func (cc *ClientConn) updateConnectionError(err error) {
cc.lceMu.Lock()
cc.lastConnectionError = err
cc.lceMu.Unlock()
}
func (cc *ClientConn) connectionError() error {
cc.lceMu.Lock()
defer cc.lceMu.Unlock()
return cc.lastConnectionError
}
|