deque操作总结
文章目录
deque操作和vector操作基本相同
构造函数
-
default (1)
explicit deque (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type()); -
fill (2)
explicit deque (size_type n); deque (size_type n, const value_type& val, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type()); -
range (3)
template <class InputIterator> deque (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type()); -
copy (4)
deque (const deque& x); deque (const deque& x, const allocator_type& alloc); -
move (5)
deque (deque&& x); deque (deque&& x, const allocator_type& alloc); initializer list (6) deque (initializer_list<value_type> il, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
示例:
|
|
赋值运算符
-
copy (1)
deque& operator= (const deque& x); -
move (2)
deque& operator= (deque&& x); -
initializer list (3)
deque& operator= (initializer_list<value_type> il);
示例:
|
|
迭代器

访问元素

容量

shrink_to_fit函数
void shrink_to_fit();
缩小以适合
请求容器减少其内存使用量以适应其大小。
一个deque容器可能具有比需要的更多内存来保存其当前元素:这是因为大多数库将deque作为一个动态数组来实现,该动态数组可以保留被删除元素的分配空间,或提前分配额外的容量以允许更快的插入操作。
该函数要求内存使用量适应容器的当前大小,但请求是非约束的,否则容器实现可以自由优化其内存使用。
请注意,此功能不会更改容器的大小
示例:
|
|
修改
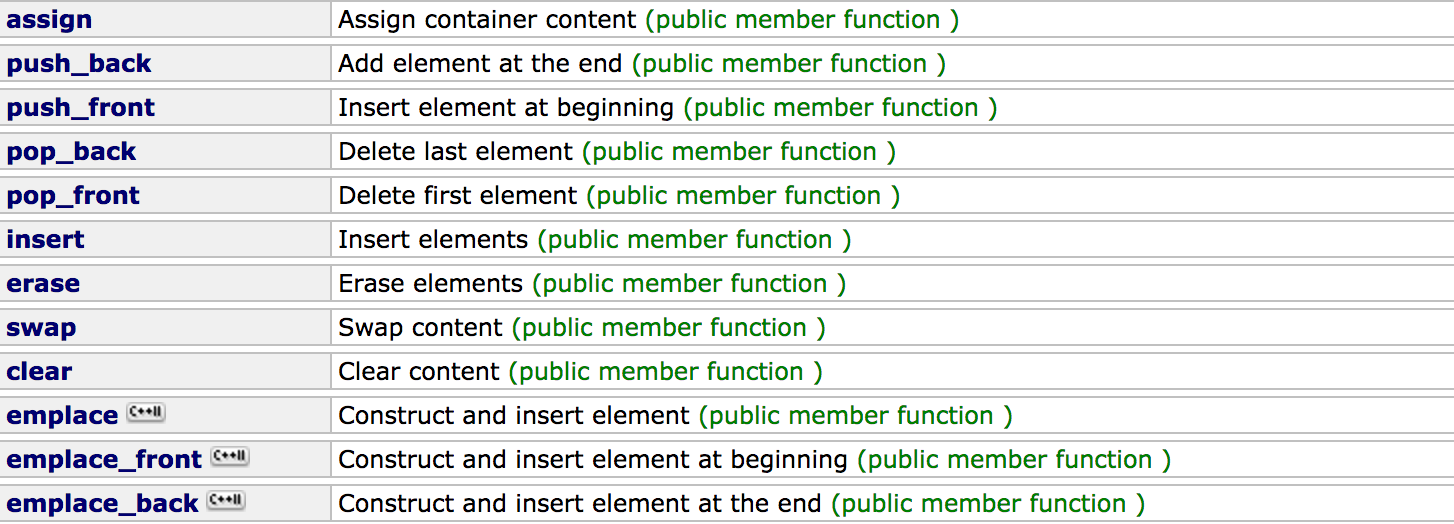 ##erase函数
##erase函数
iterator erase (const_iterator position);
iterator erase (const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
指向由函数调用erase的最后一个元素后面的元素的新位置的迭代器。
如果操作擦除了序列中的最后一个元素,则这是容器结束。
分配器

重载

##relational operators (1)
template <class T, class Alloc>
bool operator== (const deque<T,Alloc>& lhs, const deque<T,Alloc>& rhs);
(2)
template <class T, class Alloc>
bool operator!= (const deque<T,Alloc>& lhs, const deque<T,Alloc>& rhs);
(3)
template <class T, class Alloc>
bool operator< (const deque<T,Alloc>& lhs, const deque<T,Alloc>& rhs);
(4)
template <class T, class Alloc>
bool operator<= (const deque<T,Alloc>& lhs, const deque<T,Alloc>& rhs);
(5)
template <class T, class Alloc>
bool operator> (const deque<T,Alloc>& lhs, const deque<T,Alloc>& rhs);
(6)
template <class T, class Alloc>
bool operator>= (const deque<T,Alloc>& lhs, const deque<T,Alloc>& rhs);
举例:
|
|
文章作者 Forz
上次更新 2017-07-15