backoff指数退避重试算法实现
文章目录
指数退避算法
指数退避算法是适用于网络应用的标准错误处理策略,使用这种策略时,客户端会定期重试失败的请求,并不断增加各次请求之间的延迟时间。客户端应对发送到 Memorystore for Redis 且返回 HTTP 5xx 和 429 响应代码错误的所有请求使用指数退避算法。
退避算法就是网络上的节点在发送数据冲突后,等待一定时间后再发,等待时间是随指数增长,从而避免频繁的触发冲突。在计算机网络中,二进制指数退避算法或截断指数退避算法常常作为避免网络堵塞的一部分用于同一数据块的重发策略。发生n次冲突后,等待时间在0~2^n-1个间隙时间(slot times) 之间选择随机选择。比如,发生第一次冲突后,每个发送方将会等待0或1个间隙时间(slot times);第二次冲突后,每个发送方的等待时间将会在0到3个间隙时间(slot times) 之间任意选择;第三次冲突后,每个发送方的等待时间将会在0到7个间隙时间(slot times) 之间任意选择,以此类推,随着冲突次数的增加,发送方的等待时间将会有成倍增加的可能性。而从“截断( truncated)”的字面意思我们不妨可以猜出,到一定次数,指数运算会停止,也就是说等待时间不会再无限的增加下去。比如,设置上限n=10,则最长等待时间为1023个间隙时间。因为在等待时间内某些场景同样有冲突发生的可能性,所以一般流程会在16次重试后终止。具体的退避算法如下:
- 确定基本退避时间,它就是争用期(总线上的单程端到端传播时延记为 x,以太网的端到端往返时间2x)。以太网把争用期定为51.2us。对于10Mb/s以太网,在争用期内可发送512bit,即64字节。也可以说争用期是512比特时间。1比特时间就是发送1比特所需要的时间。所以这种时间单位与数据率密切相关。
- 从离散的整数集合
[0,1,…,]中随机取出一个数,记为r。重传应推后的时间就是r倍的争用期。上面的参数k按下面的公式计算:k=Min[重传次数,10]可见当重传次数不超过10时,参数k等于重传次数;但当重传次数超过10时,k就不在增大而一直等于10。 - 当重传达16次仍不能成功时(这表明同时打算发送的数据站太多,以致连续发生冲突),则丢弃该,并向高层报告。例如,在第1次重传时,k=1,随机数r从整数{0,1}中选一个数。因此重传推迟的时间是0或争用期,在这两个时间中随机选择一个。若再发生碰撞,则重传时,k=2,随机数r就从整数{0,1,2,3}中选一个数。因此重传推迟的时间是在0,2x ,4x和6x 这4个时间中随机抽取一个。同样,若在发生碰撞,则重传时k=3,随机数r就从整数{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7}中选一个数。以此类推。若连续多次发生冲突,就表明可能有较多的站参与争用信道。但使用退避算法可使重传需要推迟的平均时间随重传次数而增大(这也称为动态退避),因而减小发生碰撞的概率,有利于整个系统的稳定。
示例如下:
- 向 Memorystore for Redis 发出请求。
- 如果请求失败,请等待 1 + random_number_milliseconds 秒后再重试请求。
- 如果请求失败,请等待 2 + random_number_milliseconds 秒后再重试请求。
- 如果请求失败,请等待 4 + random_number_milliseconds 秒后再重试请求。
- 依此类推,等待时间上限为 maximum_backoff。
- 等待时间达到上限后,您可以继续等待并重试,直到达到重试次数上限(但接下来的重试操作不会增加各次重试之间的等待时间)。
其中:
-
等待时间为
min(((2^n)+random_number_milliseconds), maximum_backoff),其中,n 会在每次迭代(请求)后增加 1。 -
random_number_milliseconds 是小于或等于 1000 的毫秒数(随机值)。这有助于避免出现以下情况:许多客户端在某些情况下全部同步进行处理并同时执行重试操作,导致同步发送每一波请求。每次重试请求后,系统都应重新计算 random_number_milliseconds 值。
-
maximum_backoff 通常为 32 或 64 秒。哪个值更为适当,这取决于用例。
达到 maximum_backoff 时间后,您可以继续重试。 此后执行的重试不需要继续增加退避时间。例如,如果客户端使用的 maximum_backoff 时间为 64 秒,则在达到此值后,客户端可以每 64 秒重试一次。在某个时刻,应阻止客户端无限重试。
客户端使用的最长退避时间和最大重试次数取决于使用场景和网络条件。例如,与桌面客户端相比,同一应用的移动客户端可能需要重试更多的次数和设置更长的时间间隔。
大多数指数退避算法会利用抖动(随机延迟)来防止连续的冲突。 但是,如果使用并发客户端,抖动可帮助您更快地成功执行请求。
至于指数避退算法的场景有哪些呢?指数退避算法在计算机网络中应用很广泛,这里简单说两个场景,第一个场景,接入三方支付服务,在三方支付提供的接入接口规范中,服务方交易结束结果通知和商户主动查询交易结果都用到重发机制,这就是所谓的退避算法,这地方其实也引出了另一个知识点——接口的幂等性( 使用相同参数对同一资源重复调用某个接口的结果与调用一次的结果相同),这里不再过多赘述。第二个场景,在app应用中,很多场景会遇到轮询一类的问题,一般的轮询对于app性能和电量的消耗都是个巨大的灾难。那如何解决这种问题呢?app在上一次更新操作之后还未被使用的情况下,使用指数退避算法来减少更新频率,从而节省资源和减少电的消耗。
算法实现
原理
positive feedback: 用户总是积极重试,访问一个不可达的服务。
- 客户端需要限制请求频次,retry backoff 做一定的请求退让。
- 可以通过接口级别的error_details,挂载到每个 API 返回的响应里。


cenkalti/backoff
程序包 github.com/cenkalti/backoff/v4 实现了用于重试操作的backoff算法。
使用重试功能可重试可能失败的操作。如果重试不满足您的需求,请将功能复制/粘贴到您的项目中,然后根据需要进行修改。
有关用法示例,请参见下面的“示例”部分。
Constants
|
|
ExponentialBackOff的默认值.
|
|
Stop指示在NextBackOff()中不应再进行任何重试。
Variables
|
|
SystemClock实现使用time.Now()的Clock接口。
func Permanent
|
|
Permanent将给定的err包装在*PermanentError中。
func Retry
|
|
重试操作o直到它不返回错误或BackOff停止。o确保至少运行一次。
如果o返回* PermanentError,则不重试该操作,并且返回包装的错误。
在失败的操作返回之后,重试将Goroutine睡眠到BackOff返回的持续时间内。
Example
|
|
func RetryNotify
|
|
RetryNotify调用将通知函数通知错误,并为每次尝试失败的等待时间提供持续时间。
func RetryNotifyWithTimer
|
|
RetryNotifyWithTimer会使用给定的Timer为睡眠前的每次失败尝试调用带错误和等待时间的通知函数。传递nil时,将使用使用系统计时器的默认计时器。
type BackOff
|
|
BackOff是用于重试操作的后退策略。
func WithMaxRetries
|
|
WithMaxRetries在另一个BackOff周围创建一个包装器,如果自从上次调用Reset()以来已多次调用NextBackOff(),则将返回Stop。
注意:实现不是线程安全的。
type BackOffContext
|
|
BackOffContext是一种取消策略,在取消上下文后,该策略将停止重试。
func WithContext
|
|
WithContext返回带有上下文ctx的BackOffContext
ctx不能为nil
type Clock
|
|
Clock是返回BackOff当前时间的接口。
type ConstantBackOff
|
|
ConstantBackOff是一种退避策略,始终返回相同的退避延迟。这与指数补偿策略相反,指数补偿策略返回的延迟随着您一遍又一遍地调用NextBackOff()而变得越来越长。
func NewConstantBackOff
|
|
func (*ConstantBackOff) NextBackOff
|
|
func (*ConstantBackOff) Reset
|
|
type ExponentialBackOff
|
|
ExponentialBackOff是一种退避实现,它使用指数增长的随机化函数来增加每次重试尝试的退避时间。
使用以下公式计算NextBackOff():
|
|
换句话说,NextBackOff()将介于重试间隔之下和之上的随机因子百分比之间.
例如,给定以下参数:
|
|
下次重试尝试中使用的实际退避时间段将介于1到3秒之间,再乘以指数,即2到6秒之间。
注意:MaxInterval设置RetryInterval的上限,而不是随机间隔的上限。
如果自创建ExponentialBackOff实例以来经过的时间超过了MaxElapsedTime,则方法NextBackOff()开始返回backoff.Stop。
可以通过调用Reset()重置经过的时间。
示例:给定以下默认参数,如果尝试10次,则序列将为10,并假设我们在第10次尝试时超过了MaxElapsedTime:
|
|
注意:实现不是线程安全的。
func NewExponentialBackOff
|
|
NewExponentialBackOff使用默认值创建ExponentialBackOff的实例。
func (*ExponentialBackOff) GetElapsedTime
|
|
GetElapsedTime返回自创建ExponentialBackOff实例起经过的时间,并在调用Reset()时将其重置。
经过的时间是使用time.Now()。UnixNano()计算的。即使正在运行的报价器使用了退避策略,也可以安全地进行呼叫。
func (*ExponentialBackOff) NextBackOff
|
|
NextBackOff使用以下公式计算下一个退避间隔:
|
|
func (*ExponentialBackOff) Reset
|
|
将间隔重新设置为初始重试间隔,然后重新启动计时器。使用b之前必须调用Reset。
type Notify
|
|
Notify是错误通知功能。如果操作失败(带有错误),它将收到操作错误和退避延迟。
注意,如果退避策略声明停止重试,则不会调用notify函数。
type Operation
|
|
操作由Retry()或RetryNotify()执行。如果操作返回错误,将使用退避策略重试该操作。
type PermanentError
|
|
PermanentError表示不应重试该操作。
func (*PermanentError) Error
|
|
func (*PermanentError) Is
|
|
func (*PermanentError) Unwrap
|
|
type StopBackOff
|
|
StopBackOff是固定的退避策略,始终返回backoff.Stop用于NextBackOff(),这意味着永远不应重试该操作。
func (*StopBackOff) NextBackOff
|
|
func (*StopBackOff) Reset
|
|
type Ticker
|
|
Ticker 持有一个在BackOff报告的时间传递“滴答”时钟的通道。
当先前的操作仍在运行时,Ticker将继续到达,因此需要一段时间才能失败的操作可以快速连续地运行。
Example
|
|
func NewTicker
|
|
NewTicker返回一个新的Ticker,其中包含一个通道,该通道将在BackOff参数指定的时间发送时间。Ticker保证至少滴答一次。调用Stop方法或BackOff停止时,通道将关闭。在代码运行时,操作提供的退避策略(特别是调用NextBackOff或Reset)是不安全的。
func NewTickerWithTimer
|
|
NewTickerWithTimer返回带有自定义Timer的Ticker。传递nil时,将使用使用系统计时器的默认计时器。
func (*Ticker) Stop
|
|
Stop将关闭Ticker。停止后,将不再发送任何tick。
type Timer
|
|
type ZeroBackOff
|
|
ZeroBackOff是固定的退避策略,其退避时间始终为零,这意味着该操作将立即无限期地重试,而无需等待。
func (*ZeroBackOff) NextBackOff
|
|
func (*ZeroBackOff) Reset
|
|
举例
|
|
返回:
|
|
重试策略
当请求返回错误(例: 配额不足、超时、内部错误等),对于 backend 部分节点过载的情况下,倾向于立刻重试,但是需要留意重试带来的流量放大:
- 限制重试次数和基于重试分布的策略(重试比率: 10%)。
- 随机化、指数型递增的重试周期: exponential backoff + jitter。
- client 测记录重试次数直方图,传递到 server,进行分布判定,交由 server 判定拒绝。
- 只应该在失败的这层进行重试,当重试仍然失败,全局约定错误码“过载,无须重试”,避免级联重试。如果下游返回503,上游不会重试.
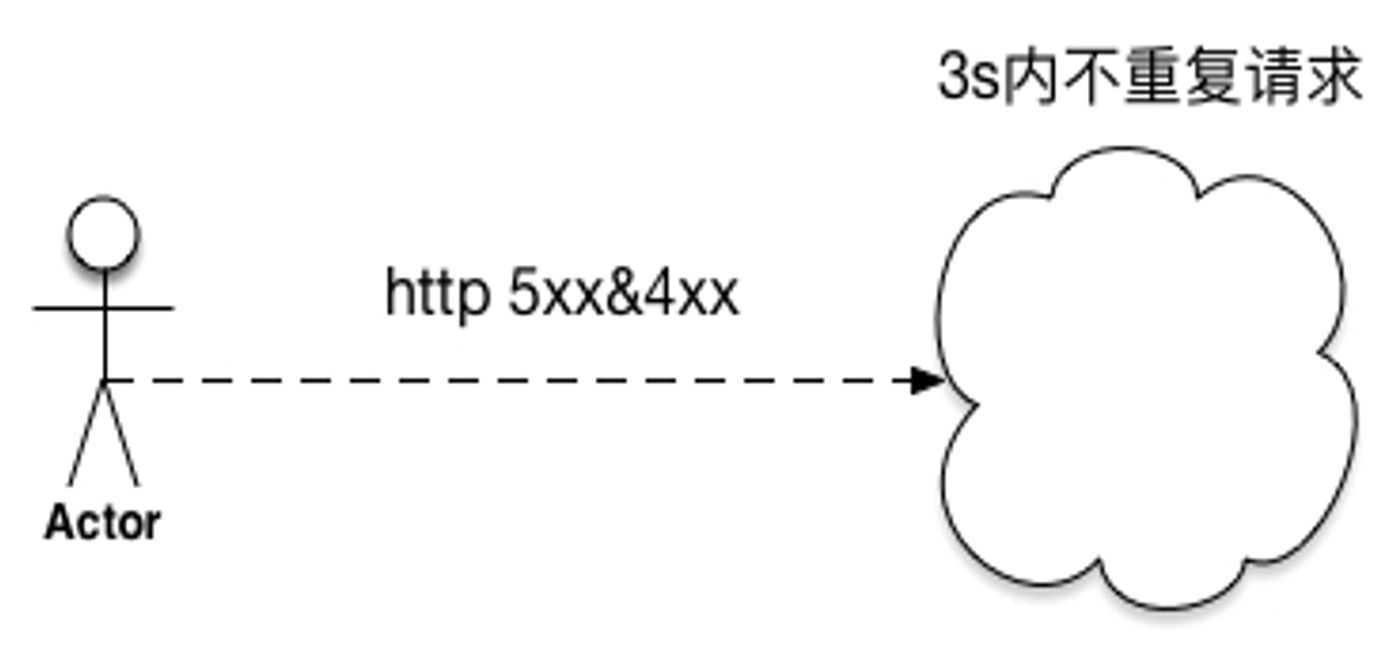
重试 - Case Study
- Nginx upstream retry 过大,导致服务雪崩。
- 业务不幂等,导致的重试,数据重复。
- 全局唯一 ID: 根据业务生成一个全局唯一 ID,在调用接口时会传入该 ID,接口提供方会从相应的存储系统比如 redis 中去检索这个全局 ID 是否存在,如果存在则说明该操作已经执行过了,将拒绝本次服务请求;否则将相应该服务请求并将全局 ID 存入存储系统中,之后包含相同业务 ID 参数的请求将被拒绝。
- 去重表: 这种方法适用于在业务中有唯一标识的插入场景。比如在支付场景中,一个订单只会支付一次,可以建立一张去重表,将订单 ID 作为唯一索引。把支付并且写入支付单据到去重表放入一个事务中了,这样当出现重复支付时,数据库就会抛出唯一约束异常,操作就会回滚。这样保证了订单只会被支付一次。
- 多版本并发控制: 适合对更新请求作幂等性控制,比如要更新商品的名字,这是就可以在更新的接口中增加一个版本号来做幂等性控制。
- 多层级重试传递,放大流量引起雪崩。
参考
文章作者 Forz
上次更新 2021-05-11